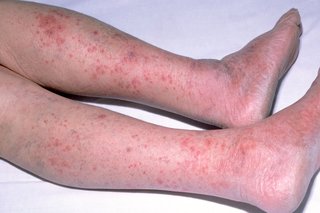
Meningococcal group B disease is the most common cause of bacterial meningitis in Ireland. Bacterial Meningitis in general occurs most often during the first month of a newborns life and is usually caused by gram-negative bacteria such as Escherichia coli or by group B streptococcus.
 18 Effects Of Meningitis On The Body
18 Effects Of Meningitis On The Body
Bacterial meningitis is inflammation of the lining that surrounds and protects your childs brain and spinal cord.

Meningitis in babies under 6 months. What increases my childs risk for bacterial meningitis. Meningitis caused by a virus is more common and usually less severe. Viral meningitis Viral meningitis doesnt respond to antibiotics so your baby will just need rest and care.
Your baby may need to stay in hospital for several days or even weeks depending on how ill she is NHS 2016a. Bacterial meningitis is most common in children who are under five years of age and in particular in babies under the age of one. Excluding a 13 year-old leukemic patient Salmonella meningitis occurred exclusively in infants 87 of them were under six months and 13 of them developed relapsing.
1415 In children younger than 3 months with unconfirmed but clinically suspected bacterial meningitis treat with cefotaxime plus either ampicillin or amoxicillin for at least 14 days. The inflammation is caused by a bacterial infection and can be life-threatening. The attack rate100000 children ranged from 192 1997 to 43 2009 with a mean of 106 and a tendency to decrease y-0689x1652.
Babies under 2 months of age are at greater risk of getting meningitis according to the American Academy of Pediatrics AAP. If the clinical course is complicated 10 consider extending the duration of treatment and consulting an expert in paediatric infectious diseases. Enteroviruses are the most common cause of viral meningitis but many other viruses can cause it.
If you think your child might have meningitis take him straight to the nearest hospital emergency department. Haemophilus influenzae type b Hib vaccine is recommended as part of the National Immunisation Program and is available free for all children at 6 weeks 4 months 6 months and 12 months of age and is administered in a combination vaccine. A vaccine is available for the meningococcal.
The bacteria are found in. Meningitis is an inflammation of the thin membranes that cover the brain and the spinal cord. Whether viral or bacterial it can be very serious and any delay in treatment could put your baby at risk for deafness intellectual disability and death.
A fungus or parasite may also cause meningitis. It is also common among teenagers aged 15 to 19 years. Between January 1994 and December 2009 167 cases of Streptococcus pneumoniae meningitis were diagnosed in children aged 1 month to 15 years.
Bacterial meningitis in older infants and children usually results from bacteria carried in the respiratory system and in newborns meningitis often comes from a bacterial infection in the bloodstream sepsis. The symptoms of viral meningitis can be very similar to those of bacterial meningitis so you must seek urgent medical help for your child if youre worried. Meningitis that affects babies up to 2 or 3 months old is called neonatal meningitis.
Some forms of bacterial meningitis can be prevented by vaccination. Although meningitis can affect people of any age babies under 2. Viral meningitis is most common in babies and young children but anybody can get it.
Bacterial meningitis is infection of the layers of tissue covering the brain and spinal cord meninges. It is most often caused by a bacterial or viral infection that moves into the cerebral spinal fluid. She should recover within a week to 10 days.
Meningitis is an uncommon but potentially dangerous infection. Children are less likely to get bacterial meningitis as they get older. In childhood meningitis Haemophilus influenzae was the most common causative organism 423 and followed by Streptococcus pneumoniae 222 and Salmonella sp 124.
Meningitis is a medical emergency and needs immediate treatment. Your baby may have headaches be grizzly and tired and reluctant to feed Wan 2017. In 2018 there were 89 cases of bacterial meningitis reported in Ireland.
Episodes of bacterial meningitis deaths associated with bacterial meningitis and sensorineural deafness requiring hearing aids and cerebral palsy following bacterial meningitis. Key points about meningitis in children. Children under two months have the highest risk of developing bacterial meningitis.
Bacterial Meningitis caused by Hemophilus influenzae type B occurs most often in infants over 1. Meningitis is inflammation of the three membranes meninges that line the brain and spinal cord. All children in Western Australia from one month to five years of age who developed bacterial meningitis over a five-year period from 1984 to 1988 inclusive.