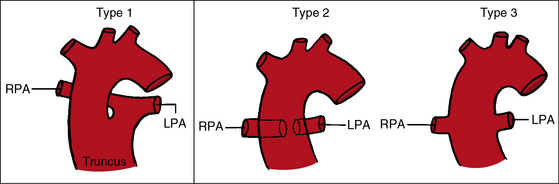
It is defined by a common origin of the aorta and the pulmonary arteries resulting from an incomplete embryologic septation and separation of the aorta and the pulmonary trunk. There are three different types of Truncus Arteriosus where the pulmonary arteries arise from the common trunk in one of several patterns.
 Truncus Arteriosus Pediatric Echocardiography
Truncus Arteriosus Pediatric Echocardiography
The second presentation is after surgical repair in childhood.
Truncus arteriosus types. Type 1 2 and 3 How can it be spotted. The Truncus Arteriosus divides into the aorta and the pulmonary arteries which carry this mixture of blood to the lungs and to the body. Such patients will definitely have problems and will require lifelong expert surveillance and management.
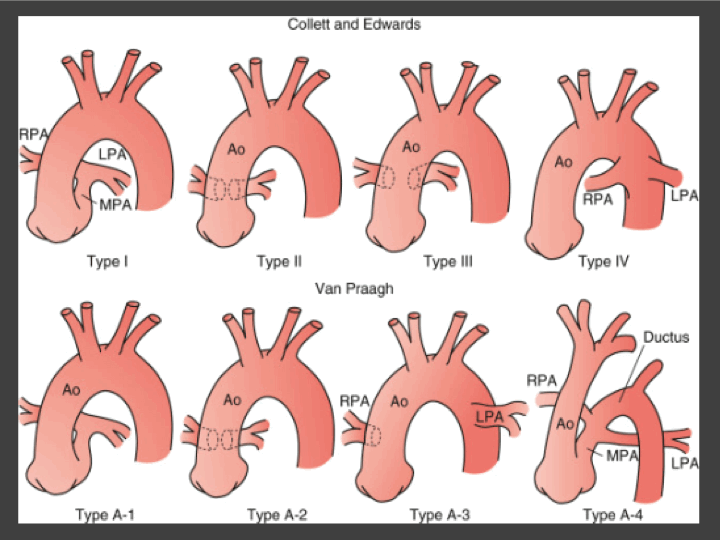
Type II- RPA LPA arteries arises directly and lying close to one another. HOW THE PULMONARY ARTERY IS CONNECTED TO THE TRUNCUS. Depending on the branching pattern of the pulmonary artery truncus arteriosus is classified into the following types described by Collett Edwards 1949.
Shunji Uchita Yorikazu Harada Kentaro Honda Koji Toguchi Yoshiharu Nishimura Tomohiro Suenaga Takashi Takeuchi Hiroyuki Suzuki Yoshitaka Okamura. Truncus arteriosus type 2 is characterized by separate but proximate origins of the left and right pulmonary arterial branches from the posterolateral aspect of the common arterial trunk. Truncus arteriosus is an uncommon but potentially lethal congenital heart disease that manifests during the neonatal period or early infancy.
The echocardiography showed truncus arteriosus type I with moderate regurgitation large pulmonary atresia large ventricular septal defect functionally single atrium moderate mitral. Type 1 - Pulmonary artery branching takes. Right and left pulmonary arteries arise separately from the posterior part of truncus type III.
The pulmonary arteries originate on each side of the Truncus Type 4. Type 2 the pulmonary arteries to the lungs. Truncus arteriosus type 1 is characterized by origin of a single pulmonary trunk from the left lateral aspect of the common trunk with branching of the left and right pulmonary arteries from the pulmonary trunk.
A single pulmonary vessel originates from the arterial trunk and bifurcates in left and right pulmonary arteries. Type IV-absence of branch of PApulmonary blood flow is derived from. In Type 1 the pulmonary artery branches arise just above the valve.
The pulmonary arteries originate from the back of the Truncus Type 3. Classification of truncus arteriosus I Edward Collett classification- Type I main pulmonary trunk arises from truncus arteriosus and gives rise to RPA LPA. Aorta and main pulmonary artery share a common arterial trunk type II.
Adult patients with truncus arteriosus may present in two ways. It is present at birth congenital heart disease. There are four sub types of truncus arteriosus which are described using two different classification systems outlined below.
Successful staged repair for a rare type of truncus arteriosus with interruption of the aortic arch and abnormal origin of the left coronary artery. The first is that they are still blue or cyanotic almost always with very high blood pressures in their lungs. Type IA1 is the most common form found in.
Truncus arteriosus is a rare type of heart disease in which a single blood vessel truncus arteriosus comes out of the right and left ventricles instead of the normal 2 vessels pulmonary artery and aorta. Type III- RPA LPA arises from separate ostium lying at some distance from one another. Truncus Arteriosus can be detected at the 20-week anatomy scan or after birth by echocardiogram.
Separate origins of the pulmonary arteries from the lateral aspect of the truncus.