Alzheimers disease AD is the most common form of dementia among older people. Alzheimers disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disease most often associated with memory deficits and cognitive decline although less common clinical presentations are increasingly recognized.
 Pdf Improvement Of Cognitive Deficit In Alzheimer S Disease Patients By Long Term Treatment With Korean Red Ginseng
Pdf Improvement Of Cognitive Deficit In Alzheimer S Disease Patients By Long Term Treatment With Korean Red Ginseng
Evidence suggests that omega-3 fatty acids may act as a possible protection factor in AD.
Alzheimer's disease articles. CERT L reduces C16 ceramide amyloid-β levels and inflammation in a model of Alzheimers disease. Doctors for Alzheimers Disease. It is the most common cause of dementia in older adults.
Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimers Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimers disease. Primary care doctors and specialists like neurologists neuropsychologists and geriatricians help support people through. While dementia is more common as people grow older it is not a normal part of aging.
Basics of Alzheimers Disease and Dementia. Bibliographies are listed by year. To evaluate the results available in the literature involving omega-3 fatty acids supplementation and its effect on.
Alzheimers disease is the most common cause of dementia a continuous decline in thinking behavioral and social skills that affects a persons ability to function independently. Olivari BS Baumgart M Taylor CA McGuire LC. Who Should Be on Your Healthcare Team.
Journal of Alzheimers Disease is an international multidisciplinary journal to facilitate progress in understanding the etiology pathogenesis epidemiology genetics behavior treatment and psychology of Alzheimers disease. The cardinal pathological features of the disease have been known for more than one hundred years and today the presence of these amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles are still. Alzheimers disease is a neurological condition in which the death of brain cells causes memory loss and cognitive decline.
Alzheimers disease AD is a neurodegeneration disorder characterized by progressive impairments of memory language reasoning and other cognitive functions. In most people with the diseasethose with the late-onset type symptoms first appear in their mid-60s. It is the most common type of dementia accounting for around 6080 of.
Alzheimer disease is a common neurodegenerative disease responsible for 60-80 of all dementias and imposing a significant burden on developed nations. Dementia is a brain disorder that seriously affects a persons ability to carry out daily activities. Ceramide transfer proteins CERTs are ceramide carriers which are crucial.
Alzheimers disease is a progressive neurologic disorder that causes the brain to shrink atrophy and brain cells to die. Alzheimers disease is an irreversible progressive brain disorder that slowly destroys memory and thinking skills and eventually the ability to carry out the simplest tasks. Alzheimers disease is an irreversible progressive brain disorder that slowly destroys memory and thinking skills and eventually the ability to carry out the simplest tasks.
Professional and scientific articles from the Alzheimers Disease and Healthy Aging Program authors whose names are in bold face. Cases of Alzheimers disease are seen in older adults ages 65 years or above. Population measures of subjective cognitive decline.
Various studies show that aging can impair the bodys self-repair mechanisms including in the brain. For those over 85 the risk increases to 50 percent 2. A means of advancing public health policy to address cognitive health.
Dysregulation of ceramide and sphingomyelin levels have been suggested to contribute to the pathogenesis of Alzheimers disease AD. Between the ages of 65 and 74 approximately 5 percent of people have Alzheimers disease. It is the result of accumulation and deposition of cerebral amyloid-β Aβ and is the most common cerebral amyloid deposition disease.
The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimers disease.
 Differential Expression Of Micrornas In Alzheimer S Disease Brain Blood And Cerebrospinal Fluid Alzheimer S Dementia The Journal Of The Alzheimer S Association
Differential Expression Of Micrornas In Alzheimer S Disease Brain Blood And Cerebrospinal Fluid Alzheimer S Dementia The Journal Of The Alzheimer S Association
 Alzheimer S Dementia Wiley Online Library
Alzheimer S Dementia Wiley Online Library
Positive Health Online Article Inflammatory Process In Alzheimer S Disease
 Epidemiology Of Alzheimer S Disease And Other Forms Of Dementia In China 1990 2010 A Systematic Review And Analysis The Lancet
Epidemiology Of Alzheimer S Disease And Other Forms Of Dementia In China 1990 2010 A Systematic Review And Analysis The Lancet
 Early Network Dysfunction In Alzheimer S Disease Science
Early Network Dysfunction In Alzheimer S Disease Science
 Journal Of Alzheimer S And Parkinson S Disease Peer Reviewed Articles
Journal Of Alzheimer S And Parkinson S Disease Peer Reviewed Articles
 Pdf Alzheimer Disease A Review
Pdf Alzheimer Disease A Review
The Canadian Review Of Alzheimer S Disease And Other Dementias
 Alzheimer S Dementia Wiley Online Library
Alzheimer S Dementia Wiley Online Library
 Pdf Medicinal Plants With A Potential To Treat Alzheimer And Associated Symptoms
Pdf Medicinal Plants With A Potential To Treat Alzheimer And Associated Symptoms
 Alzheimer S Disease The Amyloid Cascade Hypothesis Science
Alzheimer S Disease The Amyloid Cascade Hypothesis Science
 Alzheimer S Disease Dangers And Trials Of Denial The New York Times
Alzheimer S Disease Dangers And Trials Of Denial The New York Times
Journal Articles Alzheimer S Research Prevention Foundation
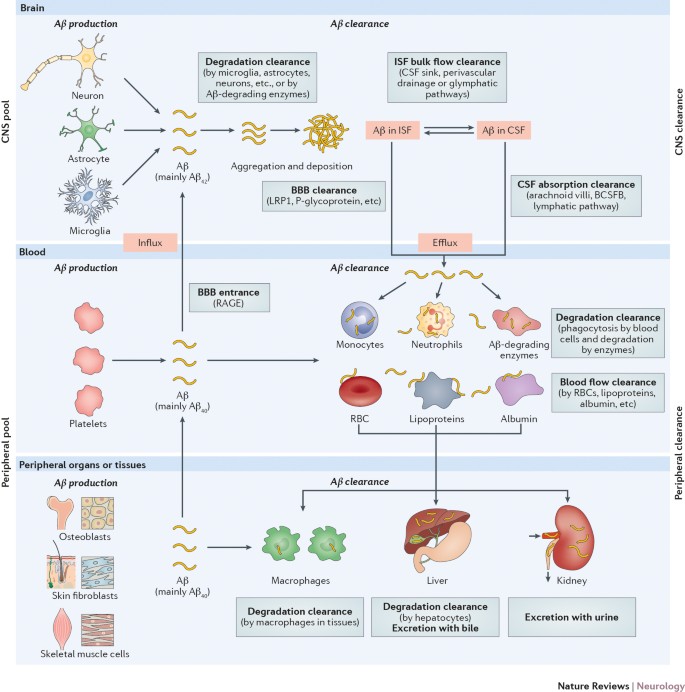 A Systemic View Of Alzheimer Disease Insights From Amyloid B Metabolism Beyond The Brain Nature Reviews Neurology
A Systemic View Of Alzheimer Disease Insights From Amyloid B Metabolism Beyond The Brain Nature Reviews Neurology
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.